A solar inverter is a crucial component of any solar power system. It converts the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is the type of electricity used in most homes and businesses. Understanding how does a solar inverter work is essential for anyone considering solar energy as a viable option for their energy needs.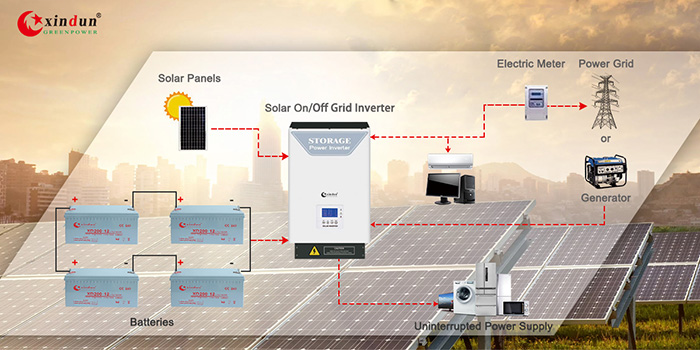
The Role of a Solar Inverter in Solar Power Systems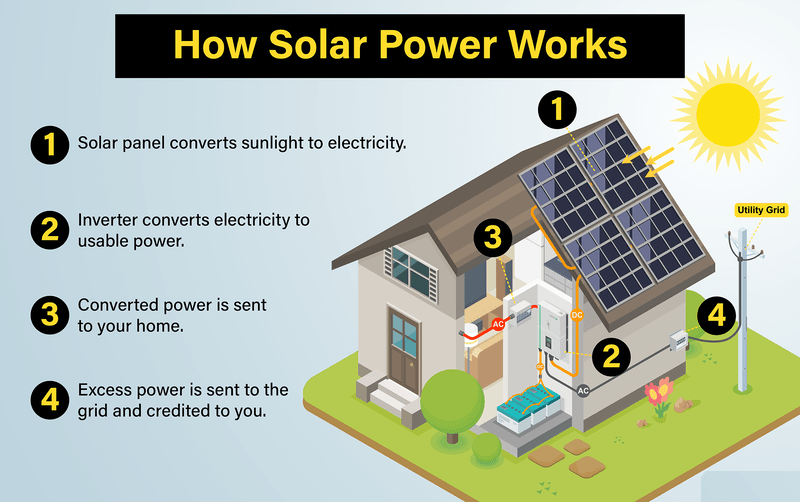
In a solar power system, the solar panels generate electricity when exposed to sunlight. However, this electricity is in the form of DC, which cannot be used directly by most household appliances. This is where the solar inverter comes into play. It not only converts DC to AC but also manages the energy flow, ensuring that your home uses solar energy efficiently.
How Does a Solar Inverter Work?
Conversion of DC to AC
The primary function of a solar inverter is to convert the DC electricity produced by solar panels into AC electricity. This process involves several steps:
- Input Stage: The inverter receives DC electricity from the solar panels.
- Inversion Process: The inverter uses electronic circuits to switch the direction of the current, effectively converting it from DC to AC.
- Output Stage: The AC electricity is then sent to your home’s electrical system, where it can power your appliances.
Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT)
One of the advanced features of modern solar inverters is Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT). This technology optimizes the amount of electricity generated by the solar panels by adjusting the electrical load to ensure that the panels operate at their maximum efficiency. MPPT allows the inverter to extract the most energy from the solar panels, especially during varying sunlight conditions.
Grid Connection and Off-Grid Systems
Solar inverters can be connected to the electrical grid or used in off-grid systems.
- Grid-Tied Inverters: These inverters allow excess electricity generated by your solar panels to be sent back to the grid. This can result in credits on your electricity bill, making solar energy even more cost-effective.
- Off-Grid Inverters: These systems are designed for homes that are not connected to the grid. They typically include battery storage to ensure a continuous power supply, even when the sun isn’t shining.
Types of Solar Inverters
Understanding the different types of solar inverters can help you choose the right one for your needs.
String Inverters
String inverters are the most common type of solar inverter. They connect a series of solar panels (or a “string”) to a single inverter. While they are cost-effective and easy to install, their performance can be affected by shading or dirt on one panel, which can reduce the overall output of the entire string.
Microinverters
Microinverters are installed on each individual solar panel, allowing for independent operation. This means that if one panel is shaded or underperforming, it won’t affect the others. Microinverters can maximize energy production, especially in installations with varying panel orientations or shading.
Power Optimizers
Power optimizers are similar to microinverters but work in conjunction with a string inverter. They are installed on each panel and optimize the output before sending the DC electricity to the string inverter. This setup combines the benefits of both string inverters and microinverters.
Benefits of Using a Solar Inverter – How Does a Solar Inverter Work?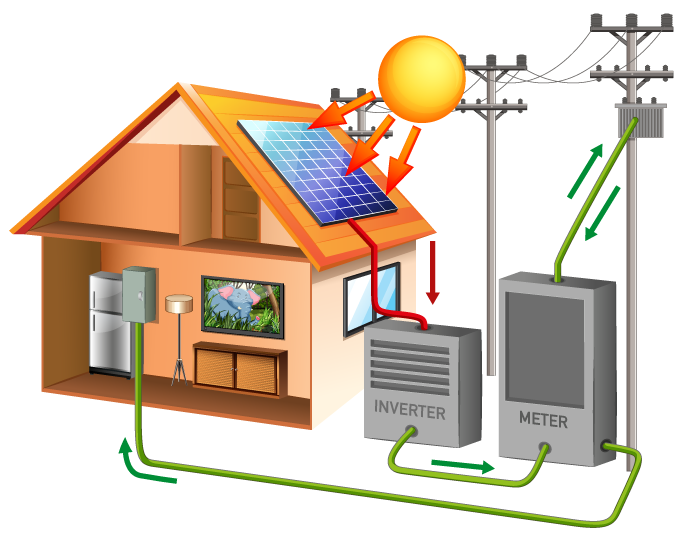
- Efficiency: Solar inverters maximize the energy output from your solar panels, ensuring you get the most out of your investment.
- Monitoring: Many modern inverters come with monitoring capabilities, allowing you to track your energy production and consumption in real-time.
- Safety: Inverters include safety features that protect your home and the solar system from electrical faults.
- Grid Interaction: If connected to the grid, inverters can help you save money by allowing you to sell excess energy back to the utility company.
Common Questions About Solar Inverters
- How long do solar inverters last? how does a solar inverter workMost solar inverters have a lifespan of 5 to 15 years, depending on the type and brand. It’s essential to check the warranty and consider replacing them as needed.
- Can I install a solar inverter myself? how does a solar inverter workWhile some homeowners may attempt DIY installations, it’s recommended to hire a professional to ensure safety and compliance with local regulations.
- What happens if my solar inverter fails? how does a solar inverter workIf your inverter fails, your solar system will stop producing electricity. Most inverters have monitoring systems that will alert you to any issues, allowing for timely repairs.
READ ALSO:
- Off Grid Solar System: Powering Your Independence
- Pure Sine Wave Inverters: The Best Choice for Your Power Needs
- Best Solar Panels for Homes: A Comprehensive Guide to Choosing the Right System
Conclusion
Understanding how does a solar inverter work is vital for anyone interested in solar energy. From converting DC to AC electricity to optimizing energy production, solar inverters play a crucial role in making solar power a practical and efficient energy source. Whether you choose a string inverter, microinverter, or power optimizer, knowing the benefits and functions of these devices can help you make informed decisions about your solar power system. If you have any questions or want to learn more about solar inverters, feel free to reach out or leave a comment below!


